# Aggregated Polling API Profile - v3.1.11
# Overview
The Aggregated Polling API Profile describes the flows and common functionality for the Aggregated Polling API, which allows a ASPSPs to deliver multiple signed event notifications to TPPs though the use of polling. It is intended as an alternative or complement to Real Time Notification in that:
- It can be used as the sole method to collect event notifications by a TPP.
- It offers a means to catch-up following a period where the TPP's Real Time Notification endpoint has been offline.
Implementation of the Aggregated Polling API is conditional for ASPSPs.
This profile should be read in conjunction with a compatible Read/Write Data API Profile, a compatible Event Notification API Profile and compatible individual resources.
# Basics
# Overview
The steps below provide a general outline of an aggregated notification flow for all resources in the R/W APIs.
# Steps
Step 1: Initial Polling
This is the first time a TPP calls the ASPSP to poll for events:
- A TPP calls an ASPSP to poll for events.
- The ASPSP responds with an array of awaiting events encoded as signed event notifications.
Awaiting events are the events that have not been acknowledgement by the TPP, or have been reported as errors by the TPP.
Step 2a: Acknowledge Only
Following the initial poll the TPP has the option to only acknowledge receipt if they do not wish to receive further events at a given time:
- A TPP calls an ASPSP to acknowledge the event notifications that have been successfully processed.
- If required, the TPP also sends indicators of event notifications which they could not process due to an error.
- The ASPSP responds positively but sends no further events.
Step 2b: Poll and Acknowledge
Following the initial poll the TPP can then repeatedly poll the ASPSP, acknowledging successfully processed event notifications and requesting more:
- A TPP calls an ASPSP to acknowledge the event notifications that have been successfully processed with appropriate parameters to receive more.
- If required, the TPP also sends event notifications which they could not process due to an error.
- The ASPSP responds positively and responds with an array of awaiting event notifications encoded as signed event notifications.
# Sequence Diagram
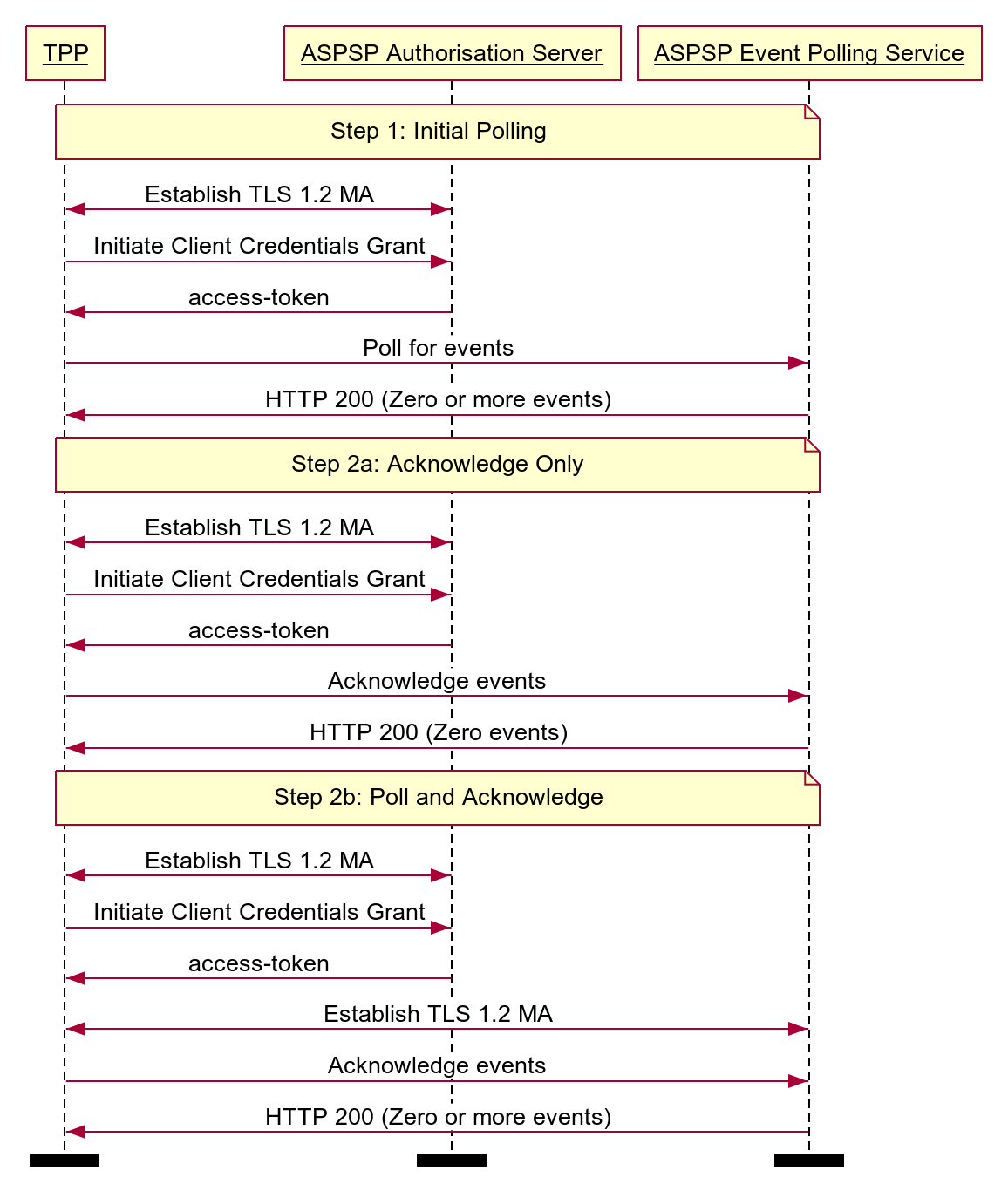
Diagram source
participant TPP
participant ASPSP Authorisation Server
participant ASPSP Event Polling Service
note over TPP, ASPSP Event Polling Service
Step 1: Initial Polling
end note
TPP <-> ASPSP Authorisation Server: Establish TLS 1.2 MA
TPP -> ASPSP Authorisation Server: Initiate Client Credentials Grant
ASPSP Authorisation Server -> TPP: access-token
TPP -> ASPSP Event Polling Service: Poll for events
ASPSP Event Polling Service -> TPP: HTTP 200 (Zero or more events)
note over TPP, ASPSP Event Polling Service
Step 2a: Acknowledge Only
end note
TPP <-> ASPSP Authorisation Server: Establish TLS 1.2 MA
TPP -> ASPSP Authorisation Server: Initiate Client Credentials Grant
ASPSP Authorisation Server -> TPP: access-token
TPP -> ASPSP Event Polling Service: Acknowledge events
ASPSP Event Polling Service -> TPP: HTTP 200 (Zero events)
note over TPP, ASPSP Event Polling Service
Step 2b: Poll and Acknowledge
end note
TPP <-> ASPSP Authorisation Server: Establish TLS 1.2 MA
TPP -> ASPSP Authorisation Server: Initiate Client Credentials Grant
ASPSP Authorisation Server -> TPP: access-token
TPP <-> ASPSP Event Polling Service: Establish TLS 1.2 MA
TPP -> ASPSP Event Polling Service: Acknowledge events
ASPSP Event Polling Service -> TPP: HTTP 200 (Zero or more events)
option footer=bar
# Acknowledgement by the TPP
draft-ietf-secevent-http-poll-01 specifies that recipients of event notifications must acknowledge them. This is manifested in one of two ways:
- Through positive acknowledgement in that the event notification has been received and successfully processed.
- Through negative acknowledgement where the event notification has been received but the TPP encountered an error in processing.
ASPSPs can evict positively acknowledged event notifications from their stores. It is implicit that TPPs are responsible for retaining a record of event notifications appropriate to their needs once positively acknowledged.
# Operating without acknowledgements
The SET standard allows the event transmitter (the ASPSP in our case) to decide how many times an event re-delivery is attempted even if it is not acknowledged
If after a period of time, negotiated between the Event Transmitter and Recipient, an SET Transmitter MAY reissue SETs it has previously delivered. The SET Recipient SHOULD accept repeat SETs and acknowledge the SETs regardless of whether the Recipient believes it has already acknowledged the SETs previously. An SET Transmitter MAY limit the number of times it attempts to deliver a SET.
If the ASPSP limits the number of times it attempts to deliver a SET to one, it can safely ignore the acknowledgements while still remaining compliant with the standard.
Similarly the TPP may safely make poll requests without acknowledging the SETs that it has received.
An ASPSP that provides aggregated polling without expecting acknowledgements must document the expected behaviour on their developer portal.
# Event Recycling Frequency
ASPSPs are responsible for documenting the frequency at which JWT Identifiers will be recycled and reused in their developer portal.
# Polling Frequency
ASPSPs are responsible for documenting the interval at which TPPs should call the polling endpoint and any further restrictions in their developer portal.
# Polling Parameters
TPPs can send two parameters to indicate the polling behaviours:
- The maximum number of events to be transmitted by the ASPSP.
- Whether the ASPSP should return a response immediately, or allow the TPP to maintain a connection to support long polling.
Given the implications of long polling (described here (opens new window)) supporting long polling is optional.
ASPSPs are responsible for documenting in their developer portal any upper bound for the maximum number of events parameter and their support for long polling.
# Security
# Authentication
ASPSPs must secure their aggregated polling endpoint using MA-TLS.
draft-ietf-secevent-http-poll-01 allows for the use signed event notifications for authentication. The conditions under which this is permissible are not met by the Read/Write API standards, so this approach should not be implemented.
# Scopes
The access tokens required for accessing the Aggregated Polling API must have one of the following scope:
accounts, fundsconfirmations, payments
# Grants Types
Consumers must use a client credentials grant to obtain a token to make POST requests to the events endpoint. In the specification, this grant type is referred to as "Client Credentials".
